
Digital Marketing {The Ultimate Guide} by a Reno Digital Marketing Expert Part 2
Chapter 2: Digital Marketing (DM)
INTRODUCTION
Marketing has come a long way since the 70s and 80s, when newspaper ads and community bulletin boards were a rage. The proliferation of digital technologies and devices, and the rise of the “connected world” has spawned new marketing paradigms. And unless you can plan, execute and evaluate the results of your marketing efforts using those digital strategies, your business will likely succumb to competitors.

WHAT IS DIGITAL MARKETING (DM)
Digital marketing is a collection of strategies and tactics that help drive prospective customers to your digital platforms. The internet has created marketing opportunities that businesses can use to sell products and services through various online venues. These digital platforms include websites, social media accounts, blogs, email and chat sites.
DM strategies are the means by which you drive awareness about your businesses’ digital presence. It includes tactics such as:
- Website marketing
- Blogs
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Email marketing
- Mobile marketing
- Search Engine ads/marketing
- Social media marketing (SMM)
- Content marketing
- Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising
- Viral video marketing
- …and much more
In short, any online activity that attempts to attract prospects to your products and services falls within the realm of DM.
HOW DOES DM WORK
So, how is DM different from traditional marketing, and how does it work?
Well, this table highlights just a few key differences between the two, and will help you understand how DM works:
| Traditional Marketing | Digital Marketing |
| One-way communication – Businesses tell prospects about their offerings | Bi-directional communication – ideally, interacts with and engages prospects about the product/service, and understands what prospects are looking for |
| Typically based on newspaper, TV or radio ads | Uses a slew of digital media, including online ads, search-driven promotions, social media, email campaigns |
| Broadcasts to a broad audience | Reaches a broad population, but can also focus on and target specific customer groups and sub-segments |
| Often focuses locally | Can target local, regional and global audiences |
| Contains a generic message to all audiences | Optimized and personalized for unique sets of audiences |

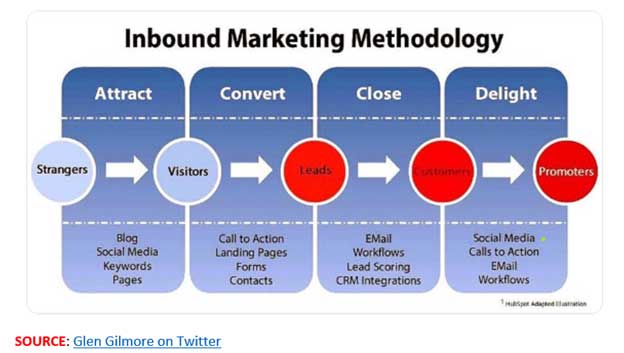
As you can see, DM is all about taking your marketing message to a wider (compared to traditional approaches) audience. Then, by personalizing that message you appeal to each individual prospects’ likes and needs for your offering. Ideally, DM is all about reaching out to strangers to convert them to paying customer. Typically, DM does this by:
- Drawing casual visitors, surfing the internet, to your online digital presences (usually a website)
- Making these casual visitors into regular visitors to that platform and others you introduce them to
- Engaging with the visitor – either in one visit or over the course of multiple visits
- Convincing them of the benefits of your offerings
- Converting them to buy from you
- Closing the deal
While traditional marketing ends once the deal closes, DM goes much further. It continues to engage clients, retain them for the long-term, and up-sell and cross-sell other products and services. Then, once clients are satisfied with your offerings, your DM strategy can leverage them (satisfied customers) to promote your offerings to their circle of friends.
WHY DM MATTERS
Because we are living in a digital world of the “connected customer”, we can’t rely on traditional marketing approaches anymore. Here’s why marketers need to embrace DM:
- DM leverages a 24×7 marketing cycle – which traditional media (newspapers, magazines) can’t!
- Your competitors are doing it…so you need to keep up!
- It offers a much better Return on Investment (ROI) than traditional marketing
- The digital sphere is where all of today’s prospects are…and that’s where you need to look for them!
- DM is easier (than traditional approaches) to implement and more accurate to measure
- It provides additional marketing opportunities, such as using social networks of prospects and clients, that just aren’t viable with traditional marketing
If you want your business to be relevant in today’s digital world, then DM should matter to you. Ignoring DM will make it extremely challenging for your business to survive and thrive.
CHAPTER SUMMARY
Digital Marketing (DM) is a marketing strategy that’s based on a collection of website promotion tactics, including SEO, Blogs, Emails, Pay-per-click (PPC), Social Media Marketing (SMM), content publishing, and more. Because consumers increasingly rely on various digital platforms to get information from, DM plays a key role in any online marketing strategy today. Contact DM specialist Sandy Rowley, at Reno Web Designer, to get your digital marketing strategy in place today!
COMMON TERMS & TERMINOLOGY
- Viral Marketing: A digital marketing strategy whereby websites encourage others (individuals and site owners) to share their content with as many others (sites and individuals) as they can
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM): A collection of DM strategies and tactics, used in combination, to get higher visibility on SERPs
- Search Engine Results Page (SERP): Denotes where (in an ascending order hierarchy) your site appears (or ranks) by a search engine. Lower numbers (#1, #2…#10 = higher rank) are better than higher (#25, #57 etc.) ones
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Measures the rate of web surfers who click on a link that takes them to a (targeted) site. Higher rates indicate more site visitor ship
- Cost per Acquisition (CPA): A marketing pricing model where advertisers (or paid ad hosts) only charge advertisers for sales leads generated or converted into actual sales (or for performing other desired action – like registration or downloads)
- Cost per Click (CPC): A pricing model where advertisers pay for every click generated by their ads – regardless of lead generation or conversion
- Conversion: The act of successfully convincing visitors to take specific action on a site. This could be making a purchase, registering for a news letter or signing-up for membership
- Organic Traffic: Refers to “free” traffic of visitors generated through search engines like Google, Bing or Yahoo. This is the opposite of paid traffic
- Impressions: Measures the number of times that a site’s targeted audience will see its ads
- Paid Traffic: Traffic typically resulting from paid advertisements on search engines, social platforms or other websites
- Keyword stuffing: A digital marketing strategy, frowned upon by most search engines, that uses an excessive number of keywords in the hope that the content or ad will gain visibility




